Parallel Computing For Python Workload
Modern day’s computer processor comes with multiple cores. Utilizing different cores often vastly reduces runtime of programs. This is helpful in the context where program manipulates large of amount of data. This tutorial will list out some ways to enable parallelization of Python code involving Pandas data frame.
JAX
Jax combines XLA and AutoGrad. It is released from Google offering the following
- Allows data manipulation on tensors
- Accelerate python code on various hardwire such as GPU/TPU by providing an optimized kernel for the custom function. Provides a Numpy wrapper.
- Accelerate single function (XLA feature)
- Accelerate entire code block similar to computation graph (jit compiler)
- Offers automatic differentiation of a python function with respect to one or many inputs. It is effective for optimizing function value
- Offers a high-level machine learning library
Some terminologies:
“A Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler is a feature of the run-time interpreter, that instead of interpreting bytecode every time a method is invoked, will compile the bytecode into the machine code instructions of the running machine, and then invoke this object code instead. Ideally the efficiency of running object code will overcome the inefficiency of recompiling the program every time it runs.” Source
“XLA (Accelerated Linear Algebra) is a domain-specific compiler for linear algebra that can accelerate Python program with potentially no source code changes. XLA provides an alternative mode of running programs: it compiles your program into a sequence of computation kernels generated specifically for the given program. Because these kernels are unique to the program, they can exploit model-specific information for optimization. It can fuse multiple operations like the addition, multiplication and reduction into a single GPU kernel. Moreover, this fused operation does not write out the intermediate values produced to memory; instead it streams the results of these intermediate computations directly to their users while keeping them entirely in GPU registers.” Source
Torchscript
It is a subset of python that are decoupled from runtime environment. It allows converting python code through simple jit call. Torchscript makes it easer to optimize code for custom hardware, quantization of machine learning model and various other optimizations.
Few other tools and libraries to parallelize python workload
Often we need to determine which part of a program takes long time to run. Instead of parallel implementation of the entire program, it is best to do parallel implemenation of the parts that are slow. Following is a demonstration of how we can profile python code.
Profile code
Typically, first step is to run a profiler to see how much time different parts of the code base are taking. I use cProfile for this purpose. snakeviz can be used to visualize the output of the profiler.
- Profile a script using the following command:
python -m cProfile -s time -o profile_output YOUR_SCRIPT.py ARGUMENT
2.a Analyze profile information using pstats
import pstats
s = pstats.Stats("profile_output")
s.strip_dirs()
s.sort_stats("time").print_stats(10)
2.b Install snakeviz
pip install snakeviz
- Visualize profiler’s output
snakeviz profile_output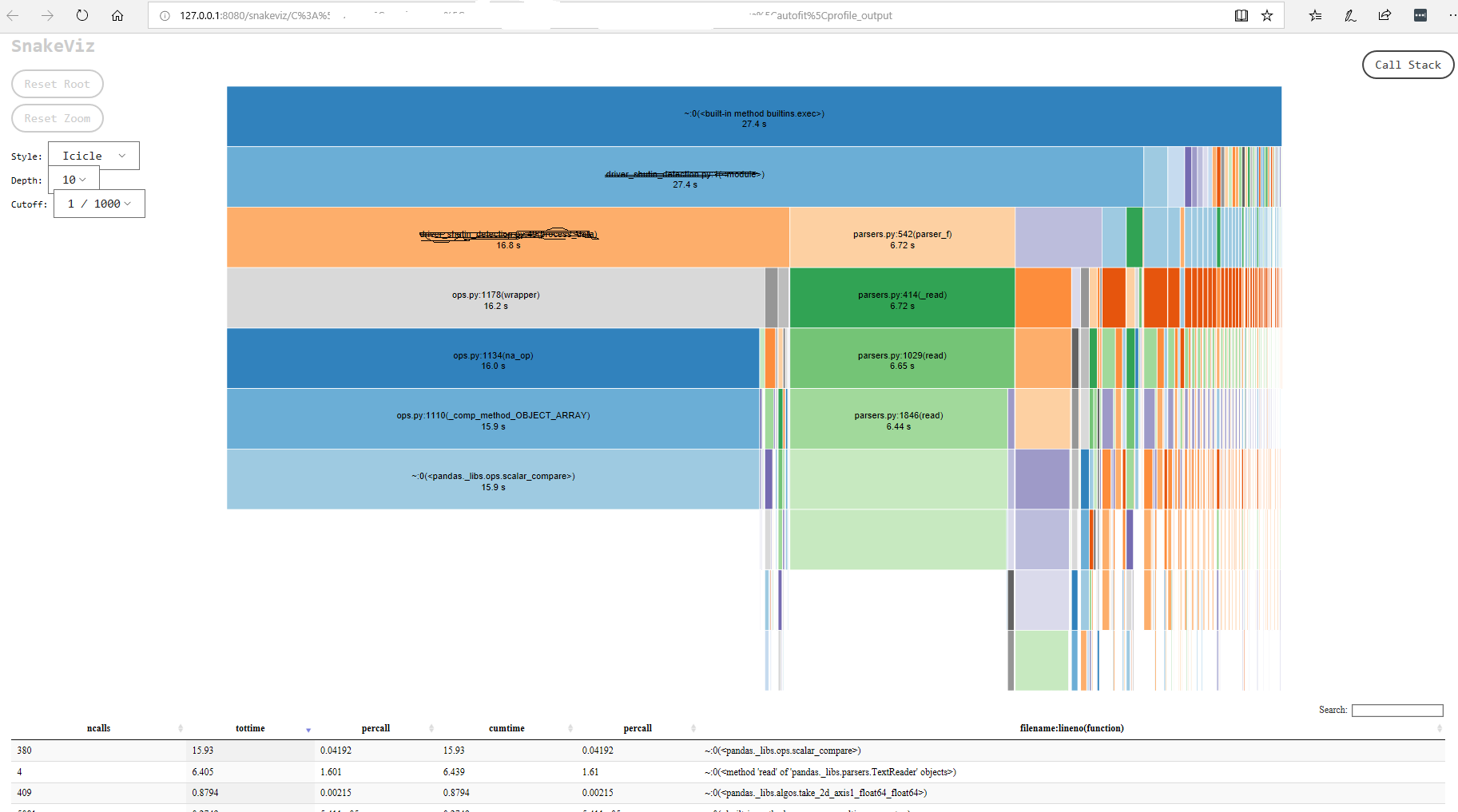
Parallel computation with an example
Partition a Pandas Data Frame
One technique that enables parallelization is to divide input data into partitions or batches. Then processing can be done in parallel on each partition.
Here input data frame is divided into 100 partitions.
NUM_PARTITIONS = 100
def data_provider(self, df):
for pi in range(NUM_PARTITIONS):
yield df.loc[df.index.values % NUM_PARTITIONS == pi]
Parallel Processing
Data partitions can be processed in parallel. Python’s Multiprocessing Module offers easy to use interfaces for parallel execution and reducing different partitions’ results. A simple process is defined that performs average operation on each item in the data frame.
def process (self, batch_df):
results = []
for i, id in enumerate(batch_df[ID].unique()):
a_df = batch_df[ batch_df[ID] == id]
results.append({id: a_df[VALUE].mean()})
return results
Finally, process can be executed in different CPU cores in parallel.
import multiprocessing
all_results = []
poolSize = multiprocessing.cpu_count() - 2
with multiprocessing.Pool(processes=poolSize) as a_pool:
for current_result in a_pool.map(process, data_provider(df)):
all_results.extend(current_result)
Dask Data Frame
Dask API offers a logical dataframe for processing large input file. It offers the same functionality as a Pandas data frame do. In Data science workflow, such data frame can greatly reduce run-time of data preprocessing. Based on the official documentation.
“Dask DataFrames coordinate many Pandas DataFrames/Series arranged along the index. A Dask DataFrame is partitioned row-wise, grouping rows by index value for efficiency. These Pandas objects may live on disk or on other machines.”
import dask.dataframe as dd
df = dd.read_csv('records.csv')
df.groupby([ID, NAME]).aggregate(['sum', 'mean', 'max', 'min'])
df.join(df, on=[MANAGER_ID, ID])
