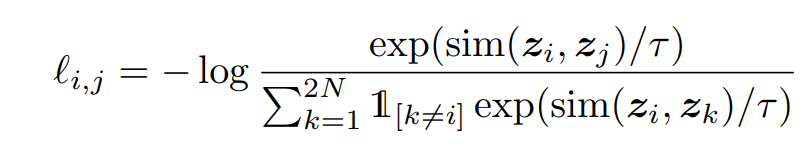Machine Learning For Autonomous Vehicle
Autonomous vehicle (AV) heavily utilizes machine learning for various tasks. Majority of these tasks are related to its perception. The perception module helps the vehicle sees the world. Recent advancements in deep learning have improved the perception for autonomous.
In this tutorial, I will describe how AV utilizes computer vision to build its perception module. Autonomous vehicles are equipped with multiple sensors such as camera, Lidar, Radar etc. Any ML model can utilize these mutli-modal datasets. I will review work that shows what data modalities to combine and when to combine in the model.
Semantic segmentation
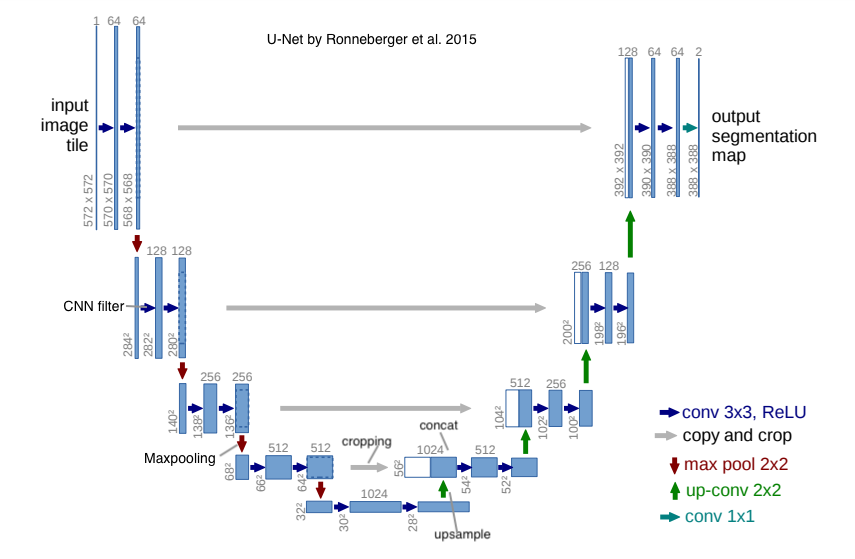
ML model divides an image into several meaningful parts in semantic segmentation. It classifies each pixel in an image into a given class. Each image comes with a mask that is the ground truth or labels of the image. Here is the model architecture typically used for semantic segmentation.
In AV, ground truth label for pixels can include road, pedestrian, forest, etc.
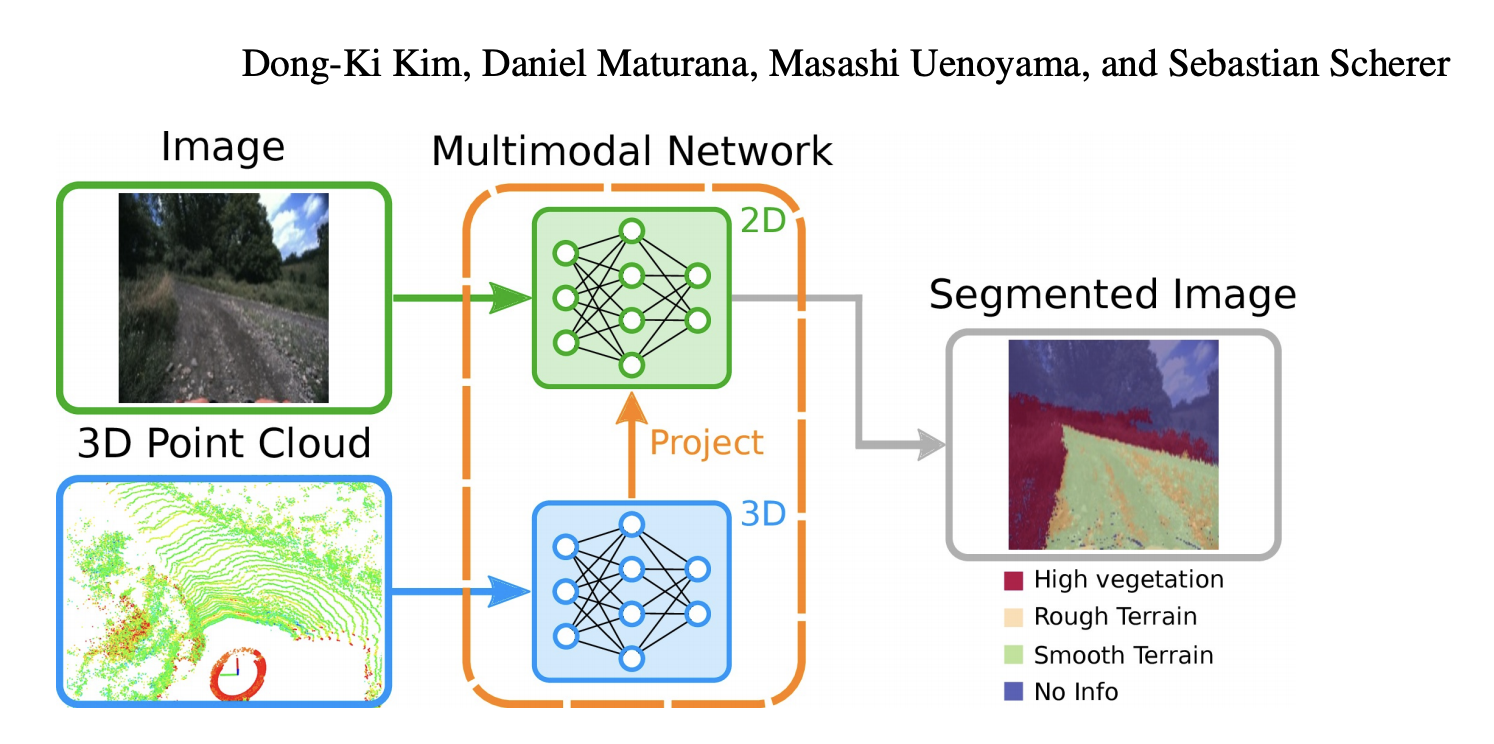 For example, Kim et al. applies two networks to process individual modality and project
LIDAR output to the image output to produce the final segmented image.
For example, Kim et al. applies two networks to process individual modality and project
LIDAR output to the image output to produce the final segmented image.
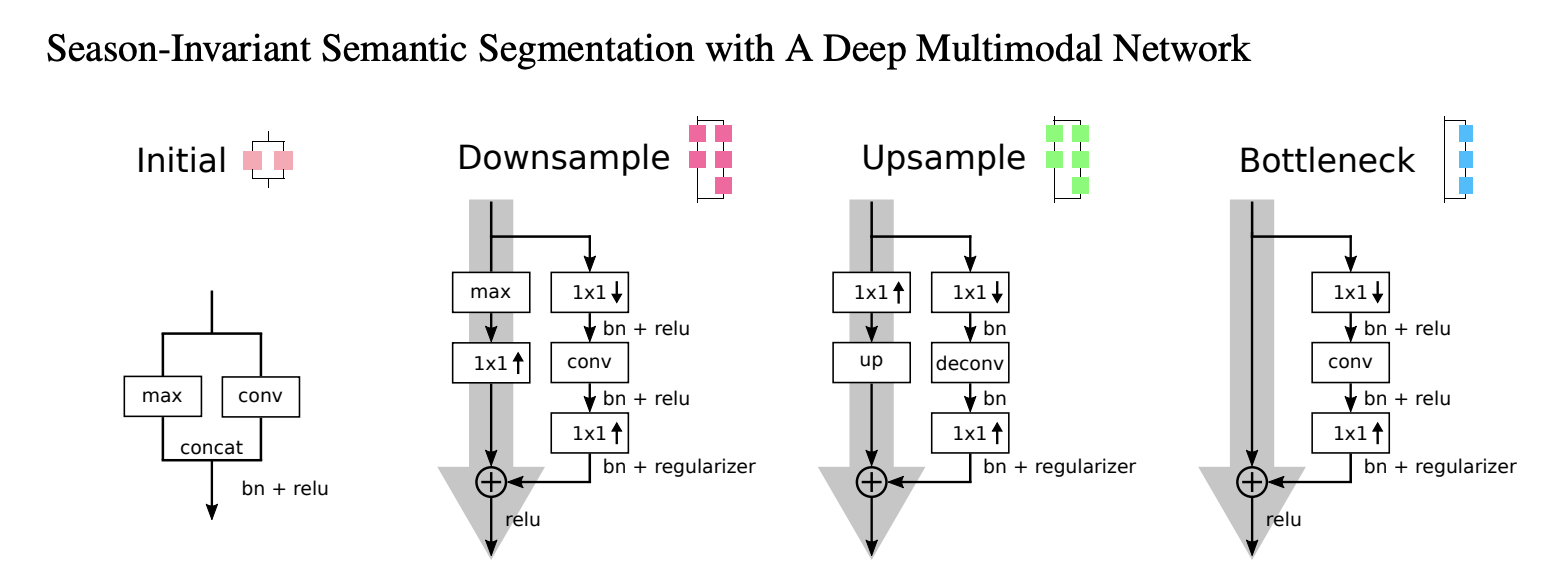 Image network learns 2D feature from images minimizing categorical cross entropy loss. It also designed to minimize inference time. It has the encoder and
the decoder layers which consist of the initial, downsample, upsample, and bottleneck layers.
Image network learns 2D feature from images minimizing categorical cross entropy loss. It also designed to minimize inference time. It has the encoder and
the decoder layers which consist of the initial, downsample, upsample, and bottleneck layers.
For the Lidar network, authors provide the roughness and the porous feature as input to the network. Since the terrain area should be smoother compared to the high vegetation area. Similarly, space containing vegetation should be more porous compared to the terrain area. Point cloud is represented by the 3D voxel grid. Network learns 3D feature representations minimizing categorical cross entropy loss in the 3D data. Network consists of 3D convolution layer, max-pooling layer, and upsampling layer.
To calculate roughness feature, a plane is fitted in each voxel. Average residual of each point from the fitted plane is the measure of roughness. Terrain tends to be less rough than forest, hilly areas. Authors also calculate porosity of each point. These high level features are projected onto 2D images by projected the 3D point location on the 2D images.
Fusion
Lidar features are fused to the image features using this network structure:
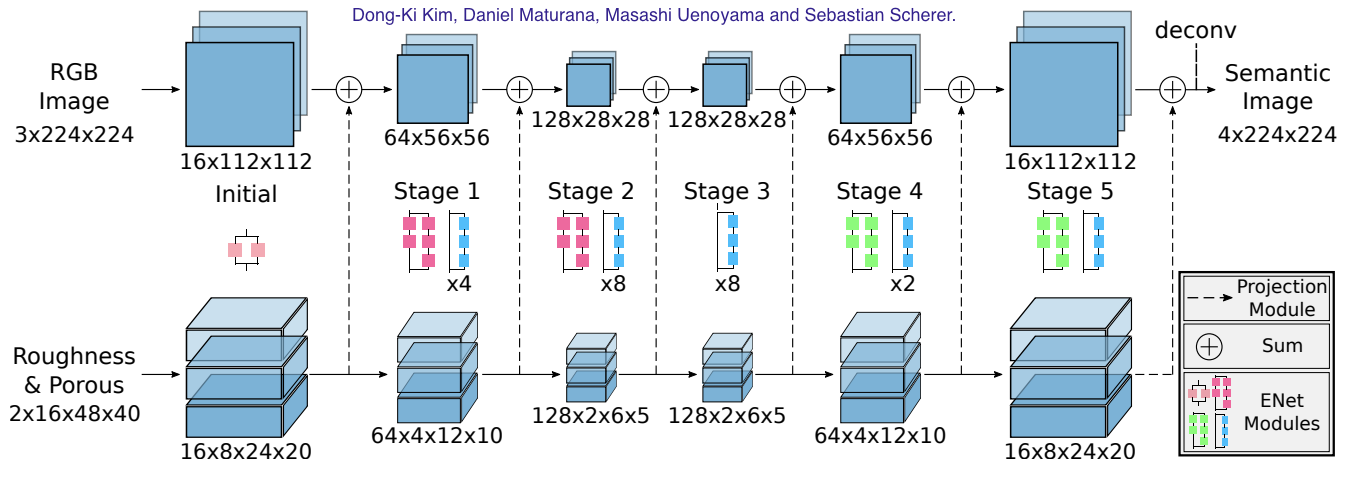
Projection of the 3D Lidar data onto the 2D images is done by a camera model. The camera model perfoms rotation as well as tranlation of the 3D points. Feature fusion is done at the multiple levels to ensure both low level and high level features are seen by different parts of the network.
Features can be fused at various other stages of the network like the following:
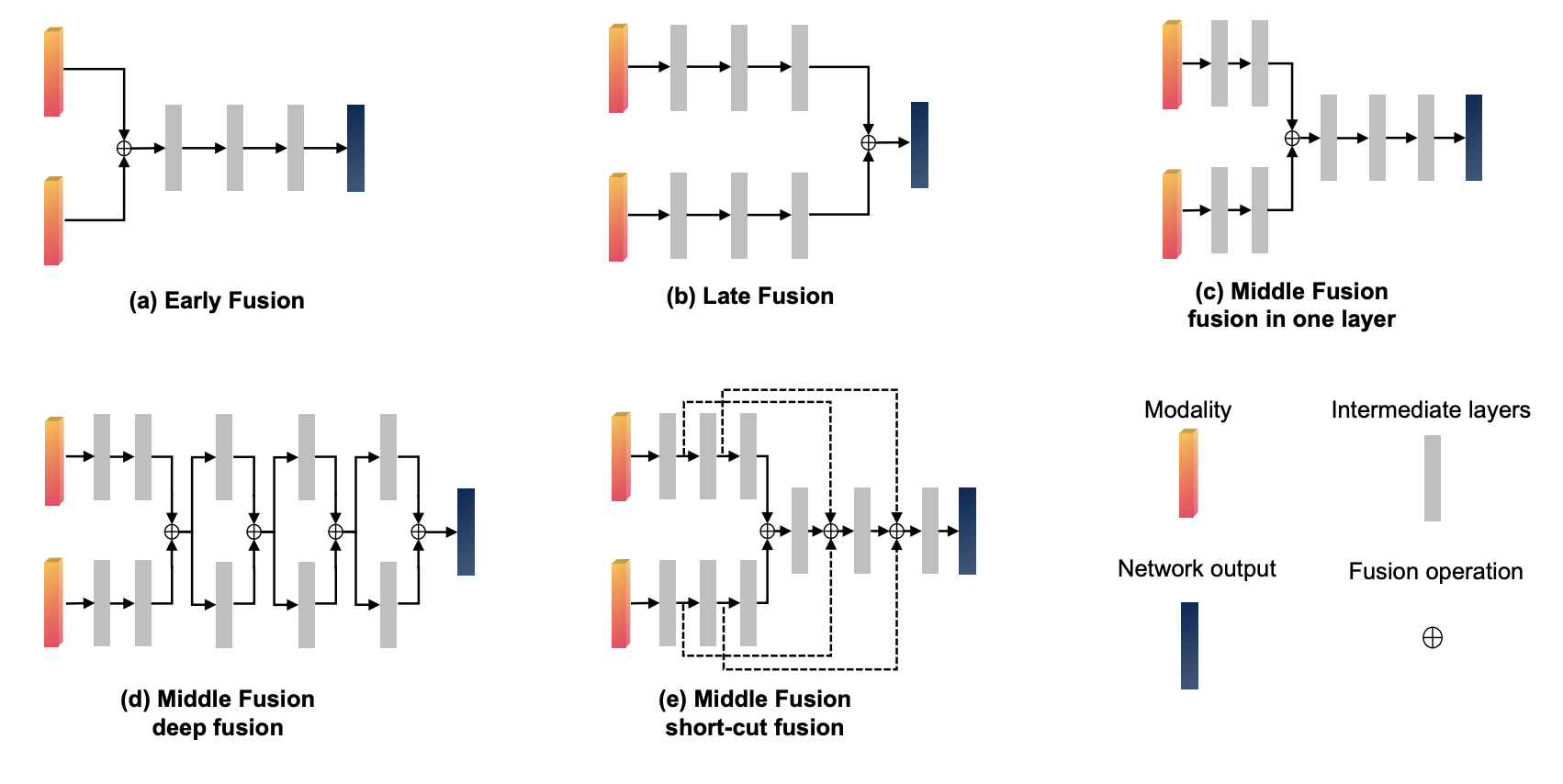
Image courtesy:
Feng, Di, et al. "Deep multi-modal object detection and semantic segmentation for autonomous driving: Datasets, methods, and challenges." IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems (2020).
Object detection
YOLO model is most commonly used for object detection which allows classifying individual entity in the image as well as bounding box around them. Recent work has show that multi-tasks help reduce inference time. For example, detecting pedestrian in a scene and predicting their intended movement in parallel helps improve the run-time performance.
Single Shot Multitask Pedestrian Detection andBehavior Prediction
by Prateek Agrawal, Pratik Prabhanjan brahman
ML4AD workshop, NeurIPS 2020
Hardware-aware detection model can help reducing latency with competitive accuracy which will result into energy savings. MobileDets finds performance improvement when a depth-wise convolution (otherwise known as inverted bottleneck layers) is used at the later stage in the Object detection model such as MobileNet and regular convolution block is used at earlier stage.
SimCLR: A simple framework for Contrastive
- Semi-supervised learning
- Objective is to create more labeled data
- It uses contrastive loss
- Same class should have similar similar embedding and different class should have different embedding.
- Same class should have similar similar embedding and different class should have different embedding.
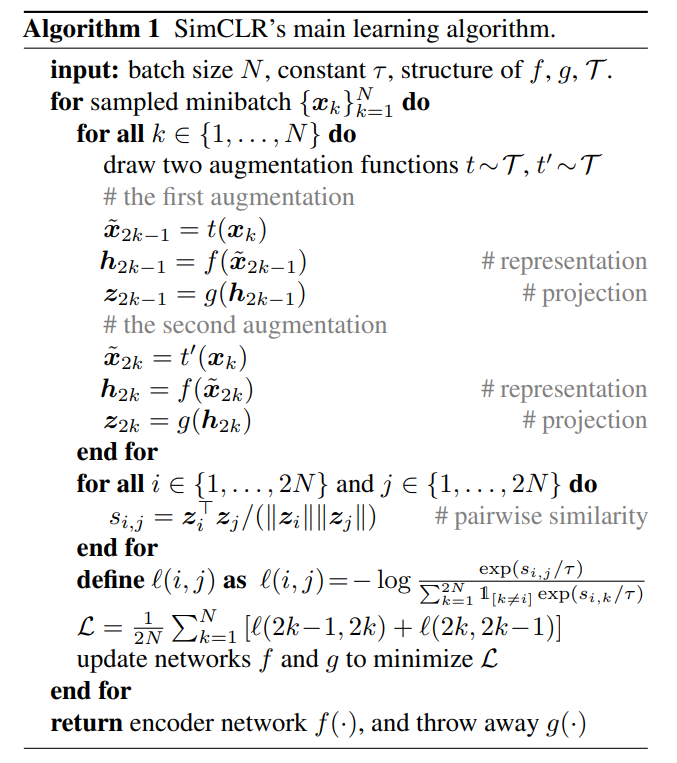
Algorithm:
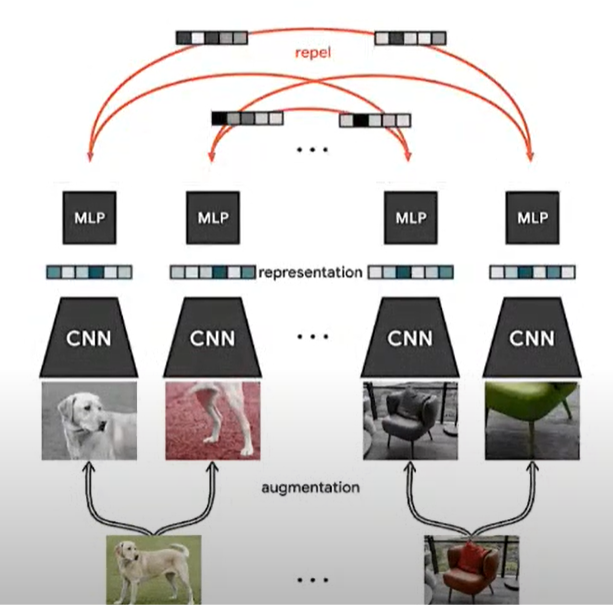
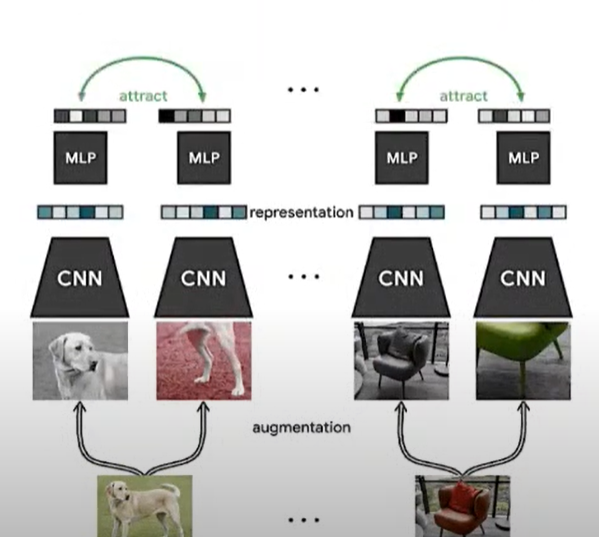
- SimCLR architecture utilizes data augmentation
- Augmention of each image is passed through ResNet model to get embedding.
- Embedding of an image should be similar to the embedding of the augmentation of the same image.
- Embedding of an image should be different than the embedding of other image or their augmentation version.
-
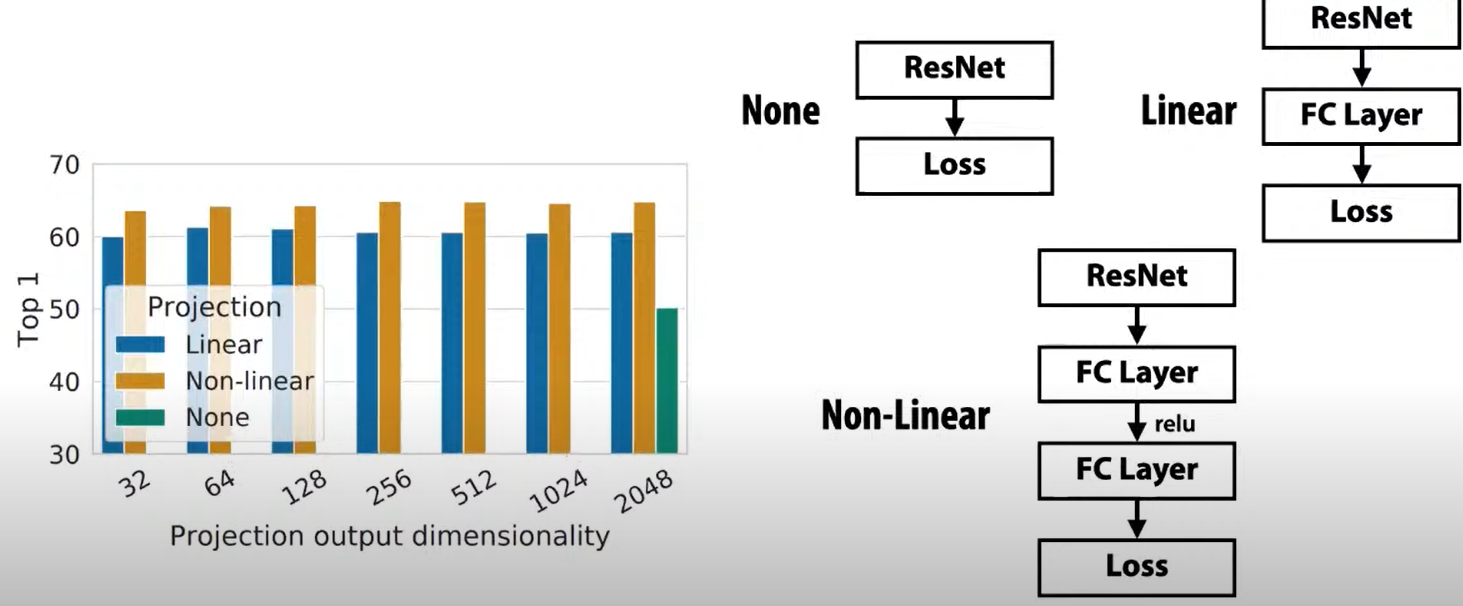
It recommends ResNet as a backbone network and apply nonlinearity.
- How to sample positive?
- How to sample negative samples?
- Random sampling is used. Unbalanced dataset can cause issues.
- Tips: Cluster similar images and sample from there.
Video discussion: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wySLC4nszv8