Machine Learning Model Inference
Inference is the process of using machine learning model to predict the outcome of a given input record. Inference typically requires low latency to ensure a smooth customer experience. This post will outline a few options for optimizing inference operation.
Optimization methods
Common optimization methods for inference before deploying the model includes
- Distillation
- Quantization
- Pruning
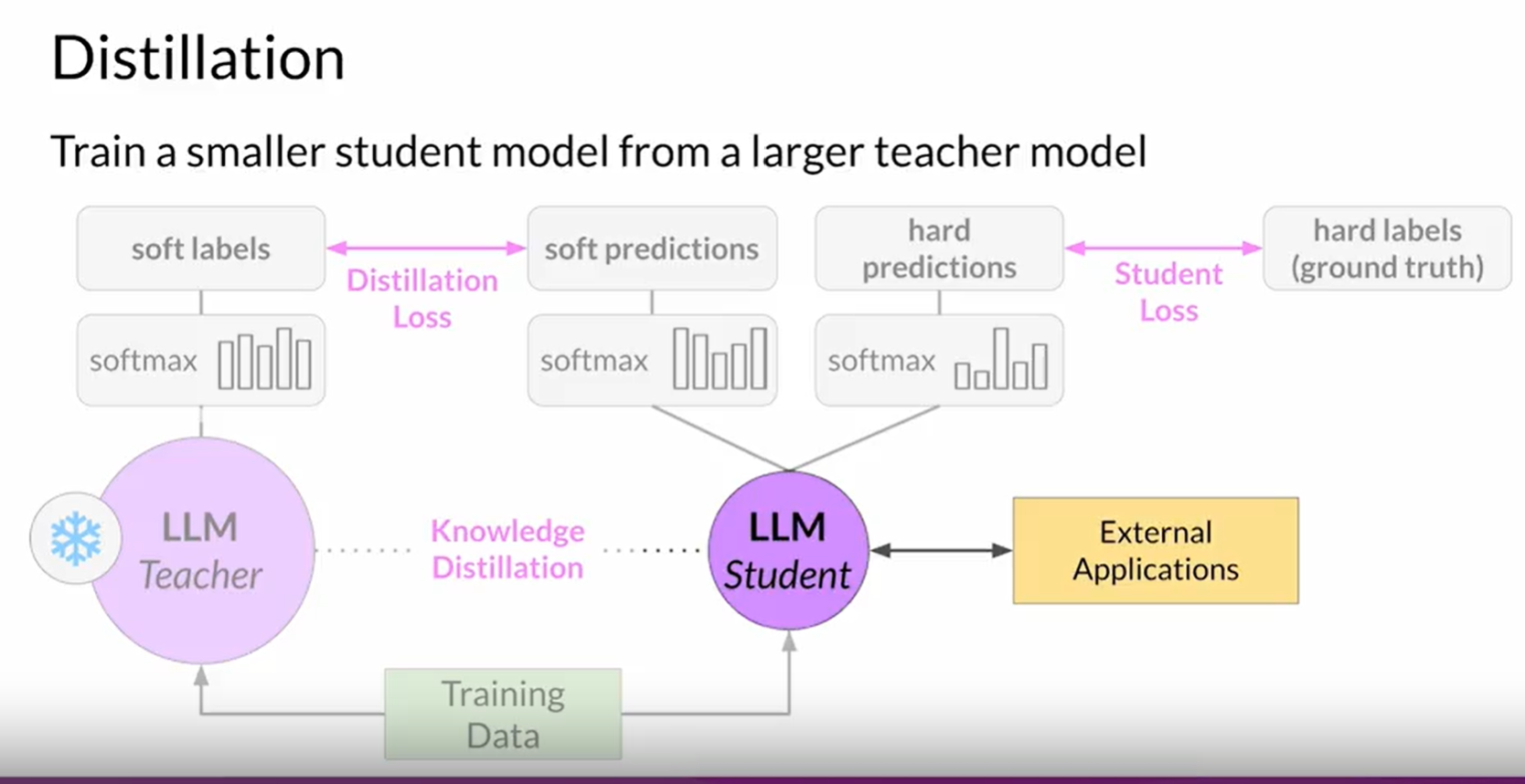
Distillation: It is process of training a smaller model mimicking the behavior of the larger model.
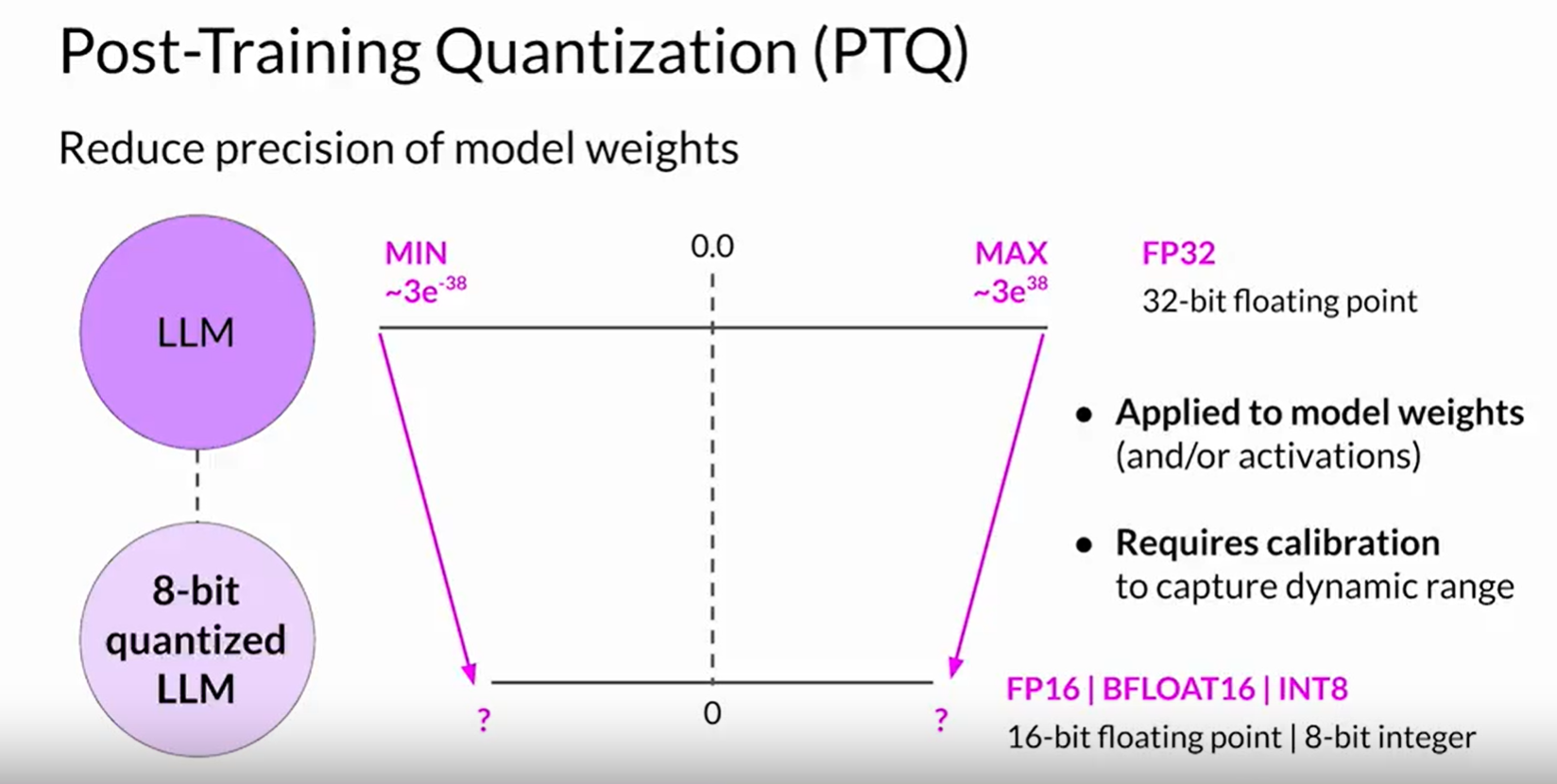
 Quantization: It uses reduced precision for floating point numbers.
Quantization: It uses reduced precision for floating point numbers.
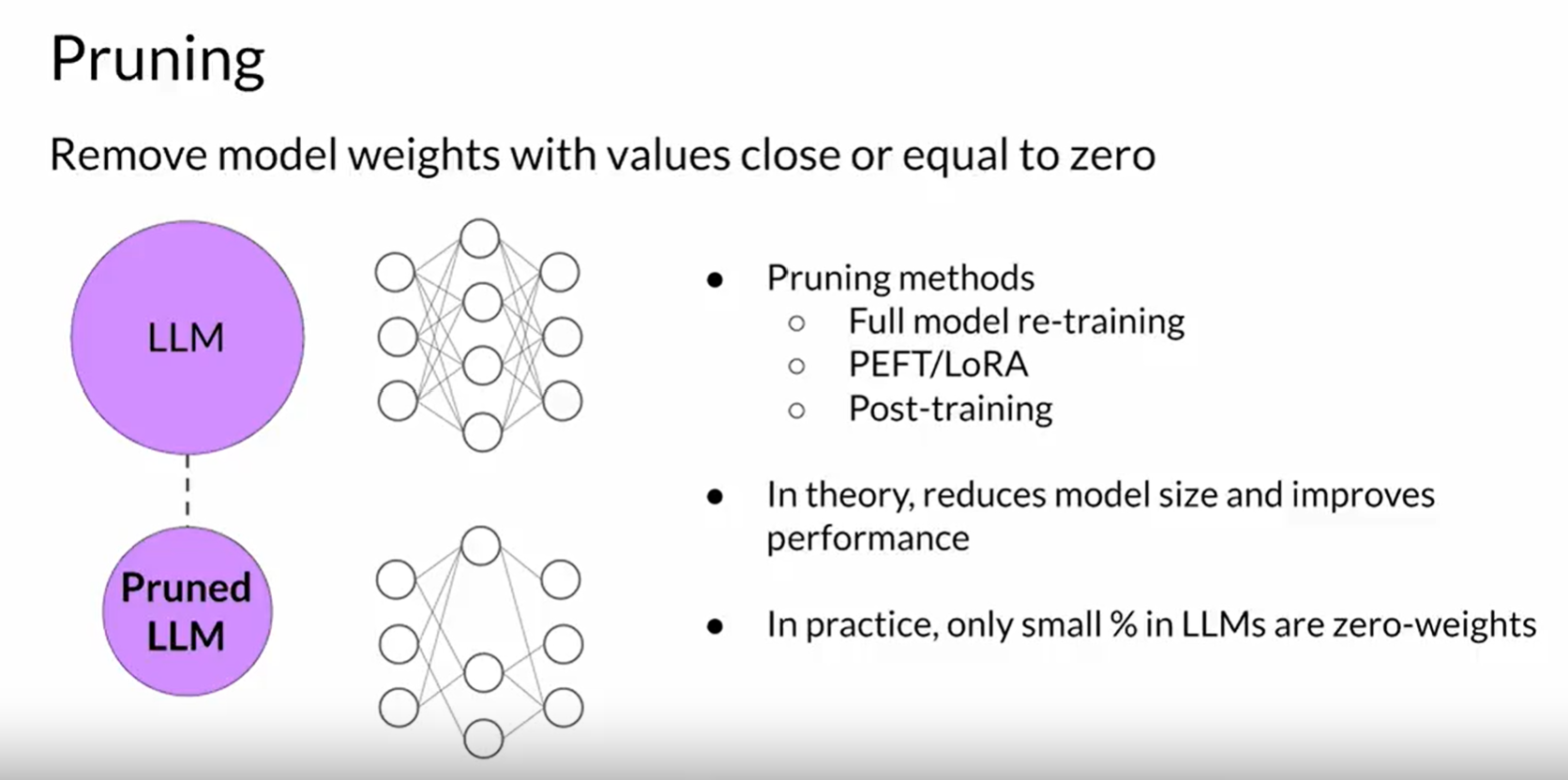
 Pruning: Remove unnecessary parts of the model that are not needed during inference.
Pruning: Remove unnecessary parts of the model that are not needed during inference.
Pytorch code optimization for inference
We can load the model in half precision. It is often required to fit a large model into memory.
For example we can load 7B parameter LLM in half precision.
# Inside GPT model class
class GPTModel:
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(<model_path>, device_map='auto',
torch_dtype=torch.float16)
tokenizer = Autotokenizer.from_pretrained(<model_path>)
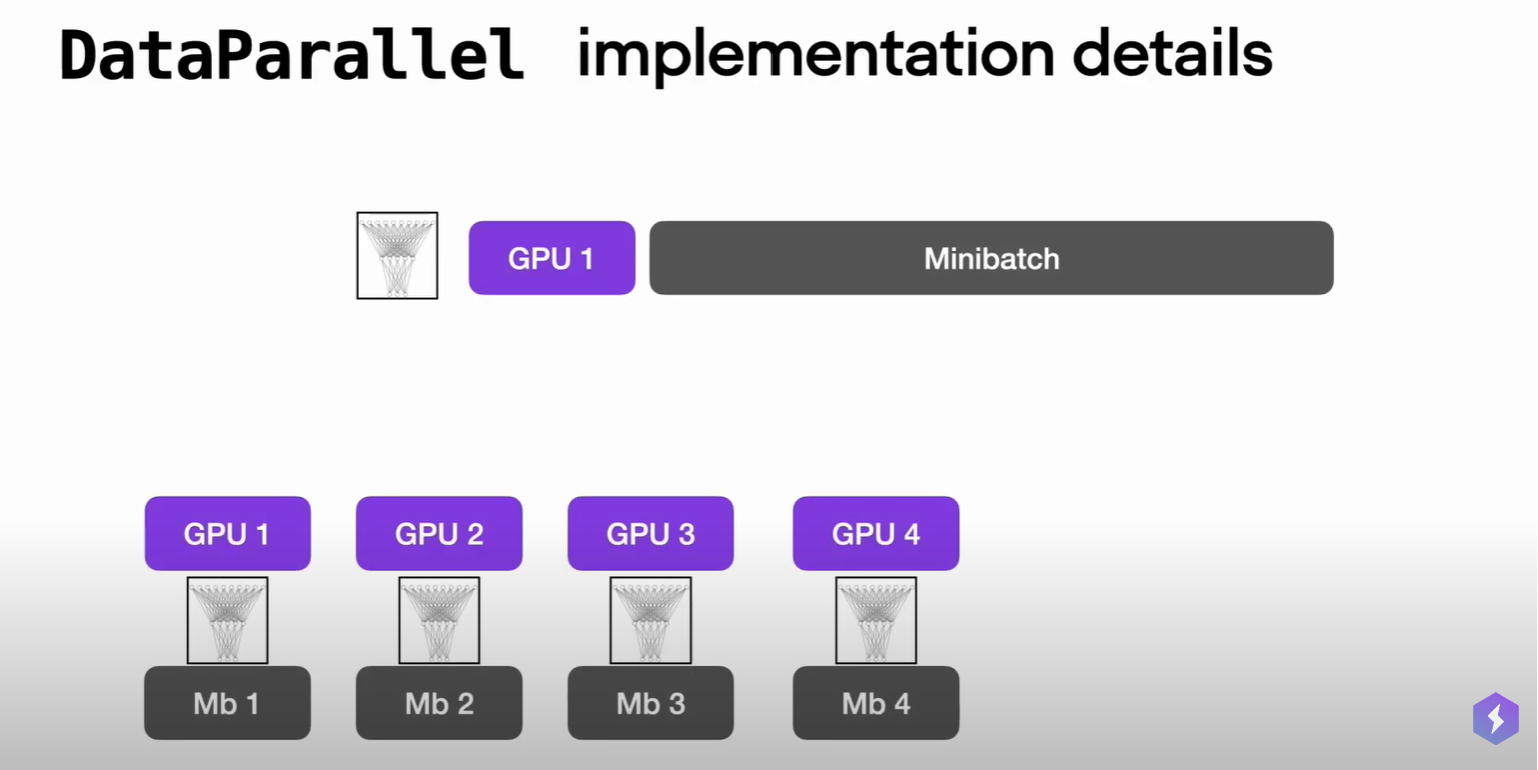
We can also wrap the GPT model object with DataParallel construct available in Pytorch. It splits the input records by the number of available GPU, copy the model into each GPU and process input record splits in parallel.
model_for_inference = GPTModel()
if torch.cuda.device_count() > 1:
model_for_inference = torch.nn.DataParallel(model_for_inference)
For data parallelism, refer to this video tutorial.
For an end-to-end example, refer to this code.
It is also important to use an optimized dataloader such as torch.DataLoader. It uses a combination of disk space and memory, instead of loading entire dataset into memory. Define the following
- Dataset: Generally defines how a raw record is tokenized. It also defines a list of input ids, attention masks and labels from a batch of raw records
- Collate function: defines how vector representation of records in a batch is stacked vertically
- DataLoader
Here is a pseudocode to illustrate the use
dataset = MyDataset(_record_getter_fn_with_yield, model_for_inference.module.tokenizer, max_length=768)
dataloader = torch.DataLoader(dataset, shuffle=False, batch_size=64, collate_fn=your_collate_fn)
Set your model to evaluate mode during inference as this will avoid unnecessary caching.
if isinstance(model_for_inference, DataParallel):
model_for_inference.module.eval()
else:
model_for_inference.eval()
Tools: ONNX runtime
ONNX is designed to allow framework interoperability and hardware optimization accessibility among other things. ONNX provides a common set of operators called opset that allows developers to move between various frameworks easily. A shared model file format provides separation between development and deployment stages, which means ML models can be deployed on a wide scale of hardware devices irrespective of the framework that was used to train the model.
Example of a transformer model being converted into ONNX format:
model = AutoModelForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
model.load_state_dict(torch.load("pytorch_model.bin", map_location=torch.device(device)))
model.eval()
# if using onnnxruntime, convert to onnx format
# ORT Python API Documentation: https://onnxruntime.ai/docs/api/python/api_summary.html
if args.ort:
if not os.path.exists("model.onnx"):
torch.onnx.export(model, \
(input_ids, attention_mask), \
"model.onnx", \
input_names=["input_ids", "attention_mask"], \
output_names=["start_logits", "end_logits"])
sess = onnxruntime.InferenceSession("model.onnx", providers=["CUDAExecutionProvider", "CPUExecutionProvider"])
ort_input = {
"input_ids": np.ascontiguousarray(input_ids.numpy()),
"attention_mask" : np.ascontiguousarray(attention_mask.numpy()),
}
input_ids = input_ids.to(device)
attention_mask = attention_mask.to(device)
model.to(device)
Given the input is a question, here is how the model is used for conversation inference
if args.ort:
# NOTE: this copies data from CPU to GPU
# since our data is small, we are still faster than baseline pytorch
# refer to ORT Python API Documentation for information on io_binding to explicitly move data to GPU ahead of time
output = sess.run(None, ort_input)
else:
output = model(input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask)
Reference Performance and Scalability: How To Fit a Bigger Model and Train It Faster
