Llm Based Agent Framework Wip
Exploring the Dynamics of Multi-Agent Frameworks: An Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, multi-agent frameworks stand at the forefront of innovation, driving systems that are more robust, adaptable, and intelligent. These frameworks represent a paradigm shift from solitary computational entities to a collective of agents, each with unique capabilities and roles, working in concert to solve complex problems. Please also read this wonderful post on agent framework.
At its core, a multi-agent framework is a system composed of multiple interacting intelligent agents.
-
Large Language Models (LLMs): These are the core of the agents’ intelligence, enabling them to understand and generate human language. They act as the reasoning engine for the agents, allowing them to process complex data and queries to produce coherent responses1.
-
Agents: These are autonomous entities within the framework, each designed to perform specific tasks and make decisions. They work collaboratively towards a shared goal, using LLMs to facilitate advanced decision-making and task execution1.
-
Tools: These are specialized functions or skills that agents use to carry out their tasks. They can range from simple data retrieval to more complex analytical functions, forming the operational backbone of the agents1.
-
Processes or Flows: These define the orchestration of tasks within the system, ensuring that tasks are distributed efficiently and aligned with the framework’s objectives. They guide both the interactions between agents and the use of tools to achieve the desired outcomes
PHIA - ReAct based framework
Mike A. Merrill, Akshay Paruchuri, Naghmeh Rezaei, et al. "Transforming Wearable Data into Health Insights using Large Language Model Agents." arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.06464 (2024).
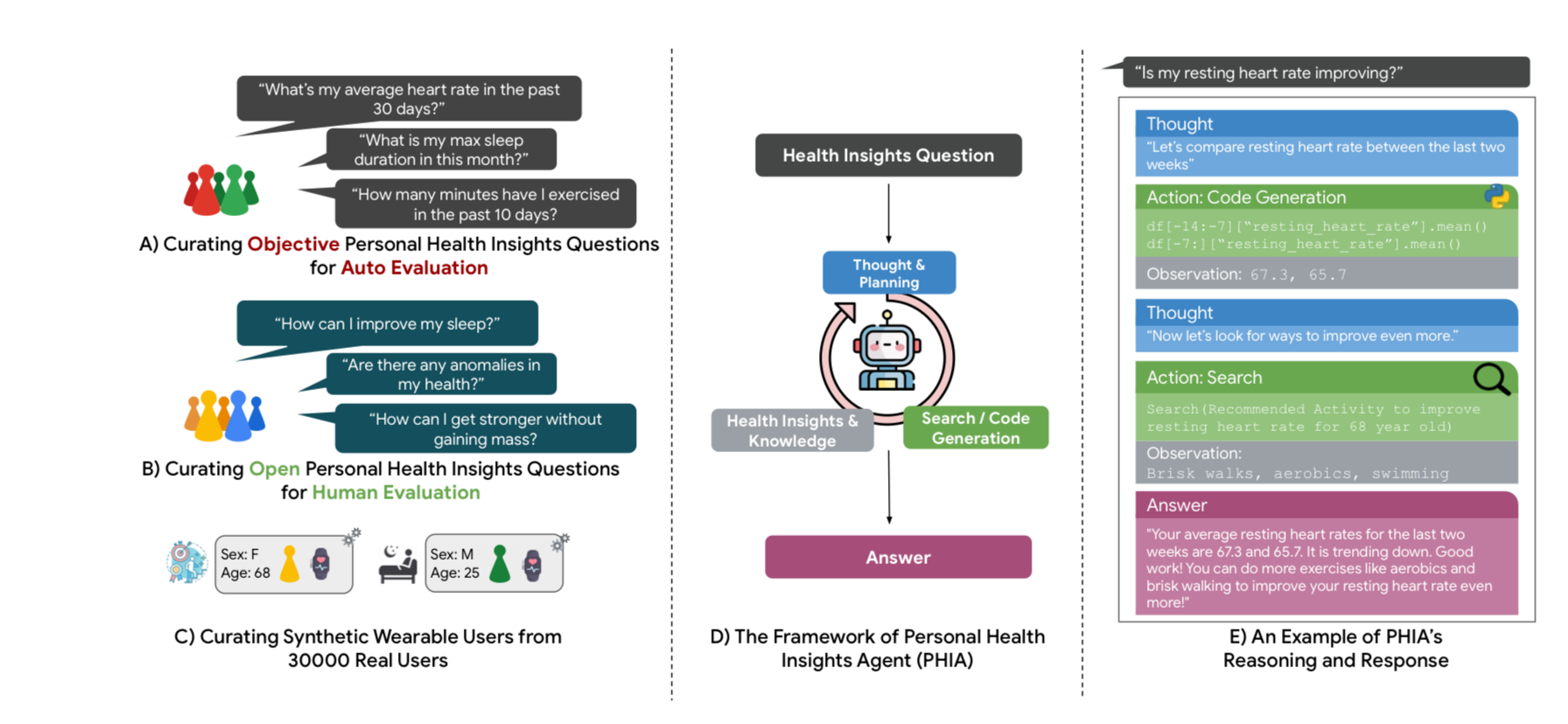
PHIA, an agent based on the ReAct framework:
Stages of Operation:
- Thought Stage: PHIA formulates a plan to address a query.
- Act Stage: PHIA uses tools like a Python data analysis runtime and a Google Search API to execute tasks and expand its health domain knowledge.
- Observe Stage: PHIA integrates the tools’ outputs into its context to enhance responses.
PHIA engages with wearable data using Python and the Pandas library for precise numerical analysis, ensuring user data privacy.
PHIA retrieves up-to-date health information from reliable web sources, improving its reasoning and credibility.
Few-Shot Prompting:
-
To master tool use, PHIA employs few-shot prompting, providing high-quality examples for task performance without extensive fine-tuning.
-
This involves computing sentence-T5 embeddings for queries, clustering them, and selecting representative queries to demonstrate high-quality responses through iterative planning and code
LLMCompiler
Kim, Sehoon, et al. "An LLM compiler for parallel function calling." arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.04511 (2023).
LangChain implementation of LLMCompiler is here.
LLMCompiler is a novel framework that optimizes parallel function calling for large language models (LLMs).
Components
- Function Calling Planner: Generates a directed acyclic graph (DAG) of tasks and their dependencies.
- Task Fetching Unit: Dispatches tasks and resolves dependencies.
- Executor: Executes tasks in parallel using associated tools.
Key Features
- Enables efficient parallel execution of multiple function calls.
- Automatically generates optimized orchestration of function calls.
- Works with both open-source and closed-source LLMs.
- Requires only tool definitions and optional examples from users.
Benefits
- Latency Speedup: Up to 3.7x compared to sequential approaches.
- Cost Savings: Up to 6.7x.
- Accuracy Improvements: Up to ~9%.
Applications
LLMCompiler can be used for various tasks requiring complex reasoning and multiple function calls, like question answering and task planning. It addresses limitations of previous sequential approaches by allowing long-term planning and massive parallelization of steps.
