Distributed Systems Review
This post will review a distributed system’s research paper:
Millions of Tiny Databases by Brooker et al.
Brooker, Marc, Tao Chen, and Fan Ping. "Millions of tiny databases."
17th {USENIX} Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation ({NSDI} 20). 2020.
The paper describes a distributed system called Physalia which is defined by the following properties.
- Distributed database
- Offers strong durability and consistency
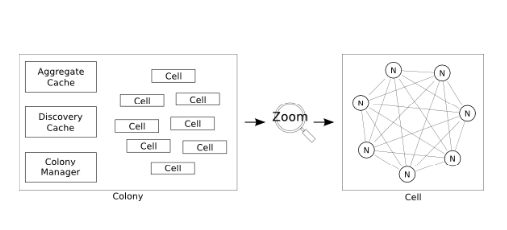
- Consists of cell where each cell consists of 7 nodes
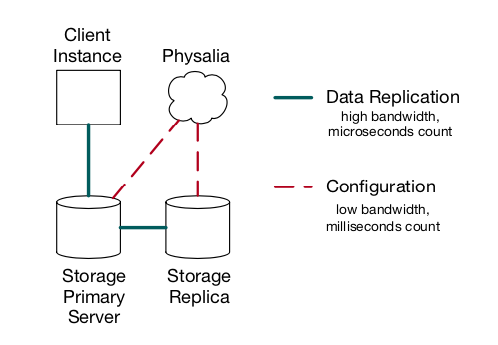
- Compute instance e.g., EC2 is Client that uses Physalia to pinpoint where blocks of a file are stored. Following is an image showing a block storage connected to a compute instance.
Paxos-based distributed state machine
- Each Physalia installation is a colony, made up of many cells
- Each cell manages the data of a single partition key
- Cell is implemented using a distributed state machine, distributed across seven nodes
- A cell is a single Paxos-based distributed state machine, with one of the nodes playing the role of distinguished proposer.
- Dividing colony into cells helps to reduce blast radius or minimize the impact of network partition.
- A node may participate in more than one cells and each cell will have many nodes.
- Each node should contain a different mix of cells, which reduces the chance of correlated failure due to load or other reasons.
Paxos algorithm overview:
This is algorithm is used by nodes in a distributed system to reach consensus on a single value. This value is later used to manage the distributed system. Goal of the system is to offer safety and liveness. I will provide a short overview of the Paxos algorithm based on the original paper:
Leslie Lamport. 2001. Paxos made simple. ACM SIGACT News 32, 4 (Dec. 2001), 51–58.
- There are two types of node: Proposer and Acceptor
- [1] A proposer first sends a prepare message with a proposal value n
- [2] When an acceptor receives a message with n, it compares n with any of the proposals it received in the past. If n is the greatest, it sends a response promising that it won’t accept any proposal with value lower than n and with the highest-numbered proposal (if any) that it has accepted.
- [3] When the proposer receives response for its request message from a majority of the acceptors, it sends an accept request to each of the acceptor containing n and v where v is where v is the value of the highest-numbered proposal among the responses, or is any value if the responses reported no proposals.
- [4] When an acceptor receives an accept request, it accepts the proposal numbered as n, except it has already responded to another prepare request with number greater than n.
Novel contribution in availability
- Address availability of the database in a unique way by
utilizing the following information
- Network topology
- Location of the client
- Data center power and networking
CAP theorem
- Primary focus is Strong consistency to ensure correctness of the storage replication protocol
- Secondary focus is availablity. It ensures Physalia is available during network partition.
Reference
Written on November 12, 2021
